Choosing the right valve for specific applications is a crucial decision that can significantly impact system performance, safety, and efficiency. Among the various types of valves available, resilient seated valves stand out due to their unique design and functionality. These valves are specifically engineered to provide excellent sealing capabilities through the use of a resilient material that enhances their performance even in challenging conditions. As industries and applications diversify, understanding the right specifications and advantages of resilient seated valves becomes essential for engineers and procurement professionals alike.
When selecting the best resilient seated valve for your application, several factors must be considered, including the media being controlled, pressure and temperature requirements, and the intended service conditions. The versatility of resilient seated valves allows them to be utilized across a wide range of industries, from water treatment facilities to manufacturing processes. By carefully assessing the operational demands and environmental factors, one can ensure that the chosen valve not only meets the technical specifications but also supports long-term reliability and cost-effectiveness.
As we explore the intricacies of resilient seated valves, it is vital to delve into their design features, advantages, and common applications. This understanding will empower decision-makers to make informed choices that can enhance system performance while also adhering to best practices in valve selection.
Resilient seated valves are critical components in various industrial applications, designed to regulate fluid flow with precision and reliability. These valves offer enhanced sealing performance due to their elastomeric seats, which provide a tight seal when closed, minimizing leakage. According to industry reports, resilient seated valves are particularly effective in water distribution systems, accounting for approximately 70% of the valve market in municipal water infrastructures. Their design allows for efficient operation in both low and high-pressure environments, making them suitable for diverse applications ranging from HVAC systems to wastewater treatment plants.
In selecting the right resilient seated valve for specific applications, factors such as pressure ratings, temperature limits, and fluid compatibility must be thoroughly assessed. The American Water Works Association (AWWA) outlines that valves should be selected based on the specific media they will handle, as different materials respond uniquely to various chemicals and physical conditions. Additionally, the operational environment, including potential exposure to corrosive substances or extreme temperatures, can significantly influence valve performance and longevity. Reports suggest that improper selection can lead to premature failure, potentially resulting in costly repairs and operational disruptions. Therefore, understanding the unique requirements of each application is essential for optimal valve performance and durability.
When selecting a resilient seated valve for your applications, several key factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and longevity. One of the primary considerations is the valve's material composition, which directly influences its resistance to corrosion and wear. According to a recent industry report by Grand View Research, the resilient seated valve market is projected to grow significantly, driven by increased investments in infrastructure and water management systems. Selecting materials that are compatible with the specific fluids and environments—such as potable water or wastewater—is crucial for preventing early failure and maintaining system integrity.
Another critical factor is the valve’s pressure rating and size specifications. As the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) sets forth, the pressure rating must align with the operational requirements of your system to prevent leaks or catastrophic failures. Choosing the correct size is equally important; too large or too small a valve can lead to flow restrictions or inefficiencies. Moreover, it's essential to consider the valve's operating temperature range, as thermal expansion can affect sealing performance. In fact, a study by the Valve Manufacturers Association indicates that improperly sized valves can lead to energy losses of up to 25%, underscoring the importance of careful selection in achieving operational efficiency.
When selecting the best resilient seated valve for your specific applications, understanding the differences among the various types available is crucial. Resilient seated valves typically feature a rubber or synthetic seating surface that ensures a tight seal, enhancing their suitability for fluid control systems. The two primary types include gate valves and butterfly valves, each possessing unique characteristics that influence performance and application.
Gate valves are often chosen for their ability to provide a low-resistance flow path when fully opened. They are ideal for applications requiring minimal pressure drop and high flow rates, such as in water supply systems. On the other hand, butterfly valves are favored for their compact design and quick operation, making them suitable for scenarios where space is limited. They excel in situations needing frequent modulation, such as in HVAC systems and industrial processes. Evaluating the operational environment, including pressure, temperature, and the nature of the media being controlled, will help determine which type of resilient seated valve will best meet your operational needs.
When selecting a resilient seated valve for a specific application, evaluating material compatibility is crucial to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and longevity. The materials used in the valve construction must align with the characteristics of the media being controlled, such as temperature, pressure, and chemical composition. For instance, if the valve is intended for use with corrosive substances, materials such as stainless steel or specialty alloys may be preferred to withstand degradation and ensure functionality.
Furthermore, the elastomer used for the seating surface of the valve plays a vital role in determining its performance in various environments. For applications involving high temperatures or aggressive chemicals, selecting the right elastomer—such as PTFE, EPDM, or nitrile rubber—is essential to prevent premature wear or failure. Additionally, considering factors such as hardness and flexibility can assist in optimizing the sealing capability and overall efficiency of the valve. Effective communication with suppliers or manufacturers about the specific application requirements can aid in making a more informed decision, ensuring the chosen valve meets the necessary durability and safety standards.
| Application | Valve Type | Material | Temperature Range (°F) | Pressure Rating (PSI) | Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water Treatment | Resilient Seated | EPDM | 32 to 140 | 150 | Water, Sewage |
| Chemical Processing | Resilient Seated | FPM | -4 to 248 | 300 | Acids, Bases |
| Oil and Gas | Resilient Seated | Nitrile | -40 to 250 | 600 | Oil, Natural Gas |
| HVAC Systems | Resilient Seated | PTFE | 32 to 180 | 150 | Chilled Water, Steam |
| Food Processing | Resilient Seated | Silicone | 40 to 250 | 150 | Food, Beverage |
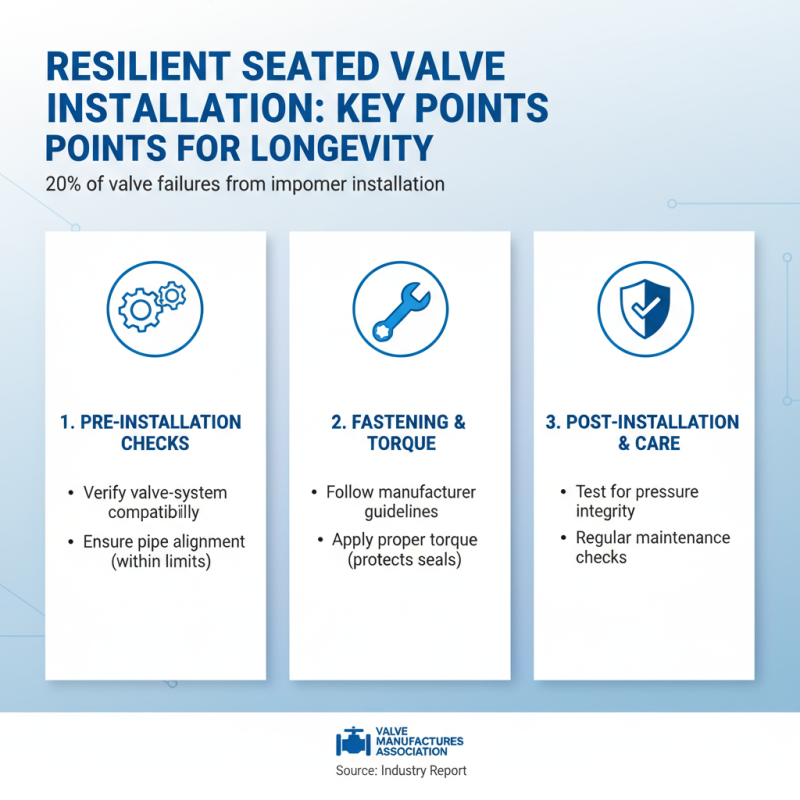
When it comes to installing resilient seated valves, attention to detail during the installation process is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. According to a recent industry report from the Valve Manufacturers Association, approximately 20% of valve failures are attributed to improper installation techniques. To mitigate this risk, it is recommended to adhere strictly to manufacturer guidelines, which often include verifying the valve’s fit and compatibility with existing systems and ensuring that pipe alignments are within tolerable limits. Additionally, employing proper torque specifications when fastening can prevent damage to the valve seals, a critical component for maintaining pressure integrity.
Regular maintenance is equally important for enhancing the lifespan and functionality of resilient seated valves. Industry best practices suggest implementing a routine inspection schedule every 6-12 months, during which valves should be checked for leaks, corrosion, and any mechanical wear. A study highlighted in the Journal of Hydraulic Engineering found that consistent upkeep can reduce operational failures by up to 30%, ultimately resulting in safer and more efficient system operations. Furthermore, flushing the valve periodically can help remove sediment build-up, which is known to impede performance. Overall, diligent installation and proactive maintenance are key strategies for achieving the best performance from resilient seated valves in various applications.